
Intraday trading has become popular among traders who want to make profits within a single trading day. Unlike long-term investing, intraday trading focuses on short price movements and requires quick decision-making. While it can be profitable, it also carries significant risk if done without proper knowledge and discipline.
What Is Intraday Trading?
Intraday trading means buying and selling financial instruments like stocks, indices, commodities, or currencies on the same trading day. All positions are closed before the market shuts. Traders do not hold any position overnight.
The main goal of intraday trading is to benefit from small price movements that occur throughout the day. Instead of waiting weeks or months, intraday traders look for opportunities that last minutes or hours.
Key points:
● Trades are short-term
● Profit targets are usually small
● Discipline is more important than prediction
How Intraday Trading Works:
Let’s break down the complete process step by step.
1. Market Opens and Price Movement Begins
When the market opens, prices start moving based on:
● Overnight global market activity
● News and economic announcements
● Demand and supply of stocks or other instruments
Intraday traders observe this early movement carefully because it often sets the direction for the day.
Some stocks move very little, while others show strong movement. Intraday traders focus only on instruments that are active and liquid, because movement is necessary to make profits.
2. Identifying Trading Opportunities
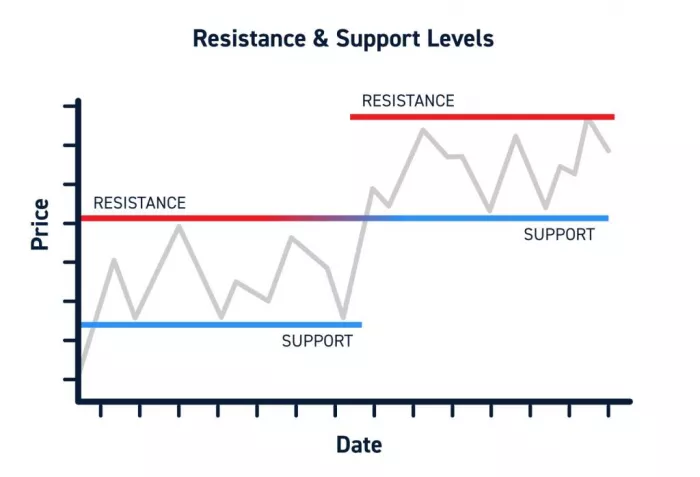
Before placing any trade, traders analyze the market using:
● Price charts
● Volume
● Support and resistance levels
● Basic technical indicators
The goal is to find a high-probability setup, such as:
● A stock moving strongly upward or downward
● A price breaking an important level
● A stock reacting to news or results
This analysis helps the trader decide:
● Whether to buy or sell
● When to enter the trade
● Where to exit if the trade goes wrong
3. Entering the Trade
Once a setup is confirmed, the trader places a trade using a trading platform. There are two main actions:
● Buy – if the trader expects the price to rise
● Sell – if the trader expects the price to fall
At the same time, the trader sets:
● A target price (where profit will be booked)
● A stop-loss (where loss will be limited)
This step is critical because intraday trading requires quick execution and discipline.
4. Role of Stop-Loss in Intraday Trading
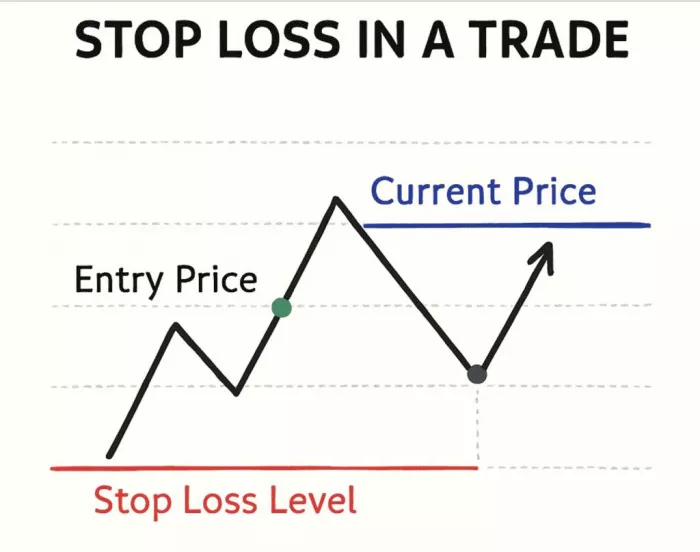
A stop-loss is a pre-defined price at which the trade is automatically closed to prevent large losses.
For example:
● If a stock is bought at ₹500
● The stop-loss may be set at ₹495
If the price falls to ₹495, the trade closes automatically.
Stop-loss protects the trader from:
● Sudden market reversals
● Emotional decision-making
● Large, unexpected losses
Without a stop-loss, intraday trading becomes extremely risky.
5. Monitoring the Trade During the Day
After entering a trade, traders closely monitor:
● Price movement
● Volume changes
● Overall market direction
Some traders exit early if:
● The market becomes weak
● The setup fails
● Volatility increases unexpectedly
Intraday trading requires active attention, especially during high-volume periods.
6. Exiting the Trade Before Market Close
One of the most important rules of intraday trading is:
All positions must be closed before the market closes.
This is done to:
● Avoid overnight risk
● Prevent losses due to unexpected news
● Comply with intraday trading rules
If a trader forgets to close a position, the broker may automatically square it off, sometimes at an unfavorable price.
7. Profit and Loss Calculation
Profit or loss is calculated based on:
● Entry price
● Exit price
● Quantity traded
Because intraday price movements are usually small, traders often use:
● Larger quantities
● Margin provided by brokers
This makes risk management even more important, as both profits and losses increase with leverage.
8. Importance of Discipline and Planning
Intraday trading does not depend on luck. It depends on:
● Having a clear trading plan
● Following rules strictly
● Accepting small losses calmly
● Avoiding emotional decisions
Successful intraday traders focus more on protecting capital than chasing profits.
Markets Suitable for Intraday Trading
Not every stock or market is ideal for intraday trading. Traders usually focus on markets where prices move actively and trades can be executed quickly.
Common intraday trading instruments:
● Stocks with high volume
● Index derivatives (like NIFTY or BANK NIFTY)
● Forex pairs
● Commodities such as crude oil or gold
High volume ensures that you can enter and exit trades easily without major price gaps.
Popular Intraday Trading Strategies
There is no single “perfect” strategy. Profitable traders stick to one or two strategies they understand well.
1. Trend Trading
In this strategy, traders follow the market direction instead of fighting it.
● Buy when the market is moving up
● Sell when the market is moving down
This strategy works well on days when the market shows a clear direction.
2. Breakout Trading
Breakout trading focuses on key price levels.
● A breakout above resistance can signal buying
● A breakdown below support can signal selling
Volume plays a major role here. A breakout without volume is often unreliable.
3. Scalping Strategy
Scalping involves making multiple small trades during the day.
● Very small profit per trade
● High number of trades
● Requires quick execution and strict discipline
This strategy is best suited for experienced traders.
4. Gap-Up and Gap-Down Trading
Sometimes stocks open much higher or lower than their previous closing price.
● Gap-up stocks may continue upward if demand remains strong
● Gap-down stocks may fall further if selling pressure continues
These trades are usually taken in the first hour of the market.
Technical Indicators Used in Intraday Trading
Technical indicators help traders understand price behavior. You don’t need to use many indicators; using too many often creates confusion.
Commonly used indicators:
● Moving Averages – Help identify trends
● RSI (Relative Strength Index) – Shows overbought or oversold conditions
● MACD – Indicates momentum changes
● Volume – Confirms price strength
Indicators should be used as support tools, not decision-makers on their own.
Risk Management: The Most Important Factor
Many traders lose money not because their strategy is bad, but because they ignore risk management.
Key risk management rules:
● Always use a stop-loss
● Risk only 1–2% of your capital per trade
● Maintain a risk–reward ratio of at least 1:2
● Avoid trading multiple positions at the same time
Protecting capital is more important than making profits. If capital survives, opportunities will come again.
Common Mistakes Intraday Traders Make
Understanding mistakes can save you from repeating them.
● Trading based on tips without analysis
● Overtrading due to greed
● Removing stop-loss out of fear
● Increasing trade size after losses
● Trading emotionally instead of logically
Successful intraday trading is more about control than excitement.
Practical Tips for Beginners
If you are new to intraday trading, follow these practical steps:
● Start with a small amount of capital
● Focus on learning, not earning initially
● Trade only during high-volume hours
● Stick to a fixed trading plan
● Maintain a trading journal to review mistakes
Learning from your own trades is one of the fastest ways to improve.
Is Intraday Trading Right for You?
Intraday trading is not suitable for everyone. It requires:
● Time to monitor markets
● Emotional discipline
● Continuous learning
If you are looking for easy or guaranteed money, intraday trading is not the right choice. However, if you treat it as a skill and respect risk, it can become a consistent income source over time.
Final Thoughts
Profitable intraday trading is not about making big profits every day. It is about small, consistent gains, controlled losses, and disciplined execution. Traders who focus on process rather than outcome tend to survive and succeed in the long run.
Learning the basics, practicing patiently, and managing risk properly can make intraday trading a rewarding experience instead of a stressful one.




Comments